DGX Spark Retrieval Augment Generation (RAG) Implementation
I am looking to create a persistent data source that AI agents can use to learn about my Store Locator Plus® web application. I want any AI agent to be able to augment their standard models with specific information about the code, development environment, user interface, and ongoing research & development notes about my project. This knowledge should be combined with standard models in order to provide better output from the AI agents.
I intend to continue to evolve the knowledge included in this data source by having it ingest published articles at public URLs as well as internally AI generated ledgers and summaries of ongoing R&D work. The concept includes leveraging the NVIDIA DGX Spark to augment this process and help serve the additional information to the AI agents.
Currently AI assistants in my developer platform talk to the deepseek-coder-v2 model running on the DGX Spark. I am now looking to now expand this by creating the “Store Locator Plus knowledge store”. This will be service via a RAG system to augment the output of the AI agents that are employed now or will be in the future. Part of the process in ensuring the data is persistent and self-controlled which is why I am starting this using the DGX Spark. Eventually it may evolve to a cloud-hosted solution.
What Is A RAG?
In simplest terms, retrieval augmented generation (RAG) provides a mechanism for AI agents to query an outside set of knowledge before it sends back a response. Most AI agents take your request, run it through an interpreter (inference engine) to determine what you mean, then send it along to a pre-trained model (like a large language model, such as GPT 5) and provide an answer based on what is already learned in that model.
Most public models are trained using insanely large server farms once or twice per year. That output is essentially a multi-gigabyte probability model that is strongly associated with a pre-defined set of data (everything it can read on the Internet, which tends to be a lot of reddit posts lately) and fixed to a specific date. As most AI agents about the newest data or when they were trained and you’ll find it to be months if not a year old. Current events, therefore, tend to be either missing or nothing but a quick AI summary of a typical Google search.
Side note: be careful what you type into a GPT prompt, if it has to go searching google large chunks of your prompts will end up in third party search bars, and thus end up in the Google search reports. There have been documented cases of this.
While general knowledge distilled out of years of Internet pages is useful for a lot of things, anything “offline” or not publicly searchable can mean significant gaps in knowledge. Just as common is the engine that does the training may deem things that are important to you “less worthy” and thus end up in the “discarded noise” of human-generated content and not even be considered by an AI agent.
RAG provides a way to force-feed your generic AI agent with topic-specific knowledge. Thus you get application-specific answers that related to your particular needs. Your requests to the AI Agent can now be handled with a lot more insight into a topic you are interested in. This is very useful for a large application like the one I have written where you want the “magic of AI” to provide better insight and analysis.
Key Points From ChatGPT Analysis
Running The RAG Service
- One RAG service
- Lives on the LAN via the DGX Spark
- An API provides the communication with the augmented data set
- POST /query → { query, top_k, filters }
- POST /ingest → feed it new docs (articles, ledgers, code snippets, changelogs, etc.)
- GET /health → for sanity checks
- A standard RAG pipeline
- Chunk and embed documentation
- Store in a vector database
- Retrieve and rerank chunks after each query
- Pass results back to the model to provide additional context
- SLP Knowledge Service (our RAG)
- Runs as a containerized micro service on theDGX Spark
- LLM Client
- Ollama + OpenWebUI
- ~OR~ NVIDIA Inference Microservices (NIM)endpoints
- talking to an LLM (i.e. deepseek coder v2)
- Embedding model
- Vector DB (Qdrant, Weaviate, Milvus, or pgvector with PostgreSQL)
- REST API (FastAPI, Node, PHP)
Build an Enterprise RAG Pipeline Blueprint article.
NVIDIA’s RAG Application in AI Workbench | DGX Spark article.
Knowledge Loading
- Define a knowledge schema, for example a JSON file that identifies each knowledge segment
Example:
{
"id": "slp-code-php-1234",
"title": "Admin UI: Location import routine",
"source_type": "code|doc|ledger|article|ticket|changelog",
"source_system": "git|glyphspeak|wp-admin|blog",
"path_or_url": "https://... or /path/in/repo",
"glyphspeak_profile": "SoftwareEnvironmentProfile",
"tags": ["admin-ui", "import", "performance", "php"],
"slp_version": "6.0.3",
"created_at": "2025-11-13T12:00:00Z",
"updated_at": "2025-11-13T12:00:00Z",
"body": "Full text of the doc/chunk",
"metadata": {
"language": "PHP",
"framework": "WordPress Multisite",
"component": "Store Locator Plus core",
"r_and_d_note": true
}
}Ingestion Pipeline
- Create scheduled ingestion job (cron / systemd)
- Pulls latest from Git repos
- Code & configuration
- AI generated ledgers (in PhpStorm / Glyphspeak)
- Crawls new articles:
- R&D Notes (internal docs site)
- Public Support site
- Main SLP News site
- Pulls latest from Git repos
- Normalize incoming data
- normalize → structured JSON (schema above)
- chunk (e.g., 1–2K tokens with overlap)
- embed chunks → store in vector DB with metadata
Connecting To AI Agents
- Most local LLM tools can be configured with a pre-call hook or “tools / extensions”
Leveraging NVIDIA Stack
- AI Workbench projects, including prebuilt RAG examples that already give you an agentic RAG service and evaluation flows
- NIM microservices + RAG Blueprint containers, which give you:
- production-ready retriever + LLM microservices
- a rag-server for orchestrating the pipeline
- standard APIs that tools can call
Recommended Path
- Minimal RAG: Python service on DGX + vector DB + Ollama/DeepSeek
- NVIDIA RAG: Switch embeddings + retriever to NeMo / NIM.
NVIDIA AI Workbench : Example Agentic RAG
Before getting too deep into building my own ingestion and parsing engines, I decided to try the built-in example RAG project on the Spark playbook site. This uses the AI Workbench with a pre-configured project, the Example Agentic RAG
After allowing AI Workbench to see devices on my local network, the Spark showed up immediately. I cloned the project as instructed, added the required API keys, started, the chat.
After a few tries I got the RAG example application working. Here are some key points to getting this online that were not immediately obvious in the documentation for this Example Agentic RAG repository.
- Get the right NVIDIA and Tavily API keys
- After opening the NVIDIA Workbench with the RAG repository loaded, go to Dashboard on the side menu.
- Expand the Get Started section and follow the links and instructions for getting the right type of NVIDIA API Key.
- Do the same for the Tavily key.
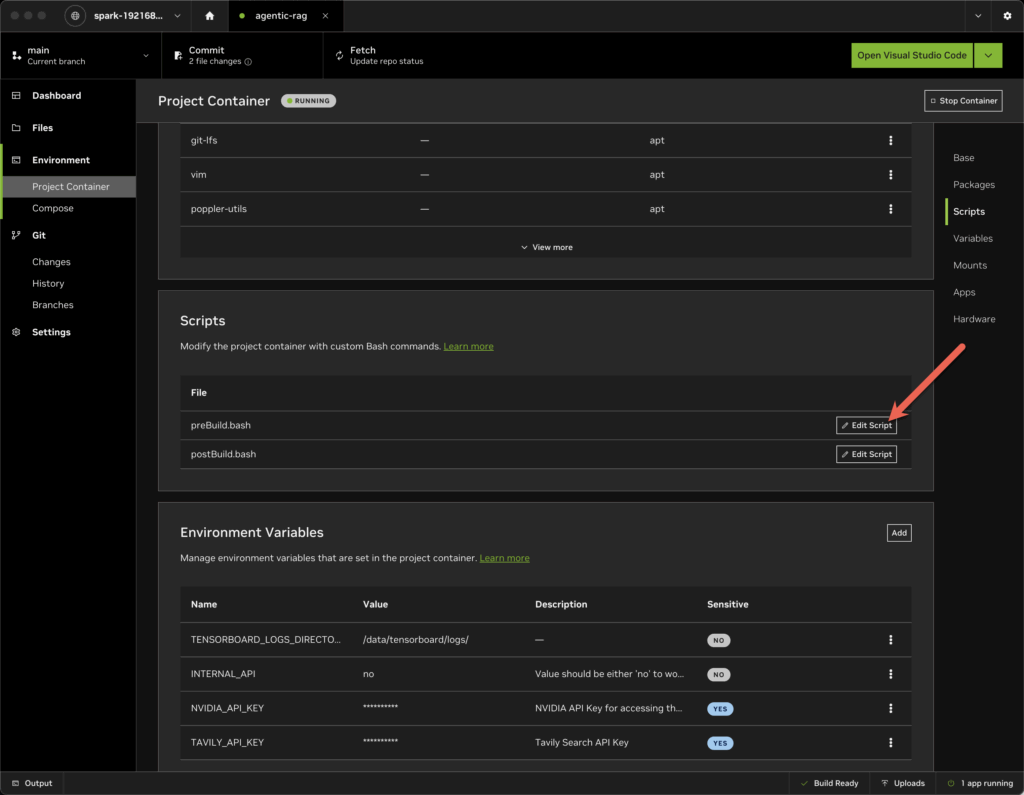
- Now go to the Environment | Project Container sidebar
- Scroll to the Environment Variable section and edit the NVIDIA_API_KEY and TAVILY_API_KEY entries.
- Force the project to use the posthog library LESS THAN 6.0.0
- There was a breaking change in version 6+ that is incompatible with this codebase.
- Open the Environment | Project Container sidebar
- Scroll down to the Scripts section of the dashboard for that project.
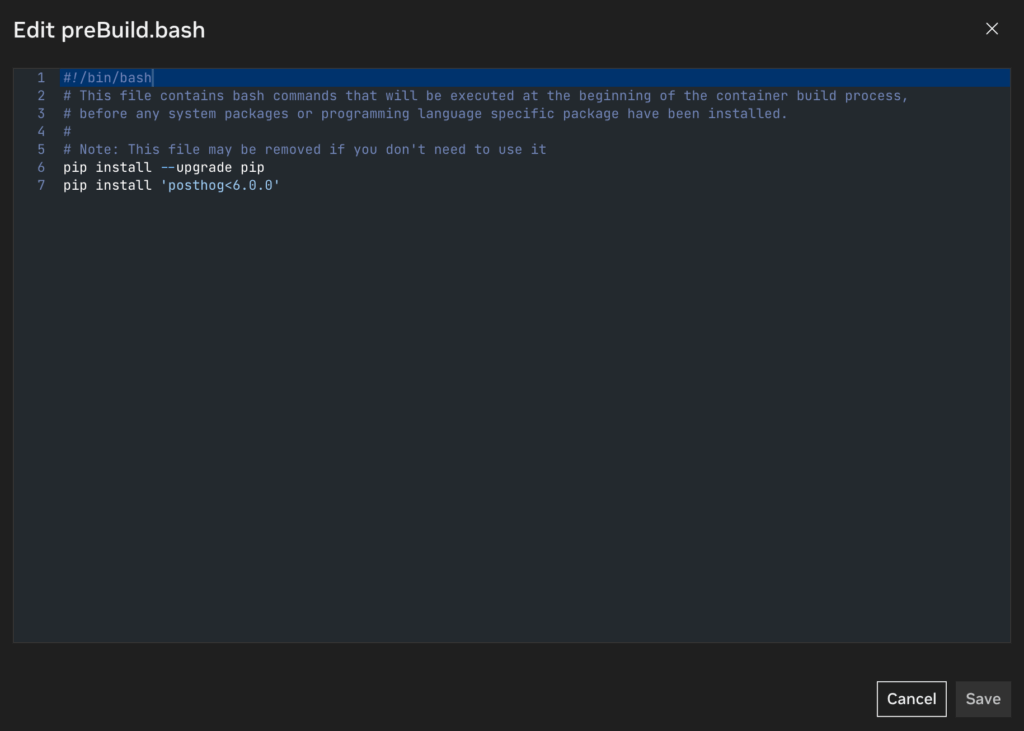
- Edit the preBuild.bash script
- Add the lines:
- pip install –upgrade pip
- pip install ‘posthog<6.0.0’
Build and start the container, then enable the chat interface via the main dashboard.
Testing The Pre-Loaded RAG
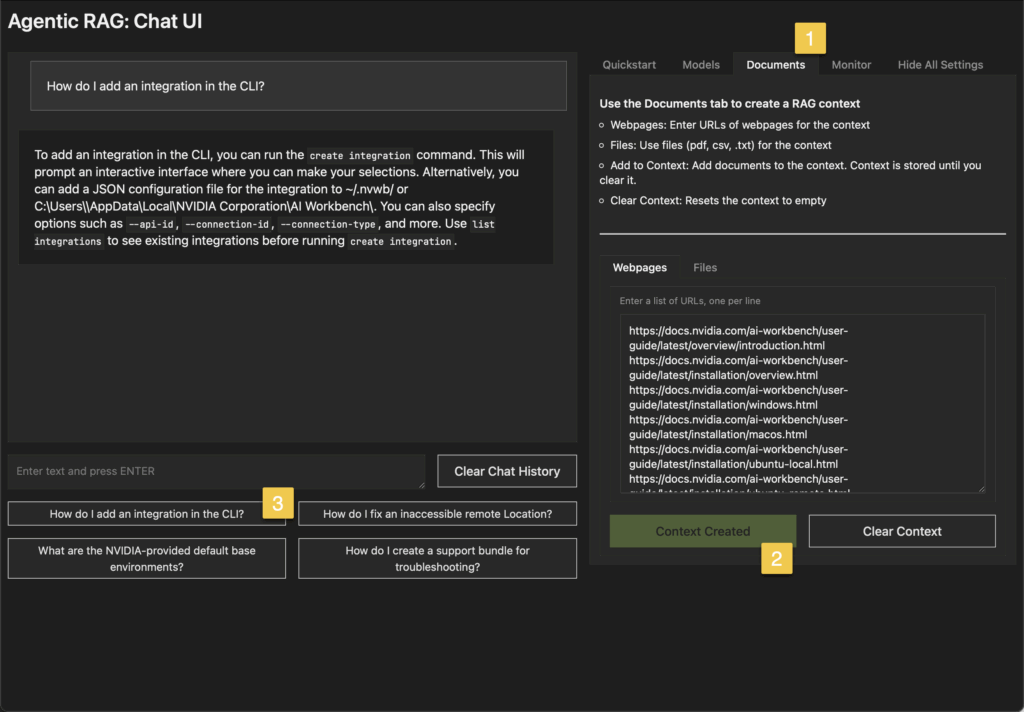
When you enable the chat a new browser window will open.
Click on the Documents tab on the right side of the interface.
With Webpages selected in the lower panel click Create Context. The button will change to “Context Created” and be “grayed out”.
This should load in the URLs and push the content into the vector database.
Now on the left panel for the chat click the pre-loaded “How do I add an integration in the CLI?” button as a test. It should reply with instructions from the online documentation.
First Attempts Failed
When I tried to attach the pre-filled URLs via the provided web-based Chat UI, it failed “No valid URLS – Try again”. I tried several things to get this working. I eventually logged into a terminal session on the Spark and ran curl against a few URLs on the list to ensure network I/O was online and able to access the outside world. It could. I rebooted, created new API keys, entered the keys, restarted the project. Same issue.
The output log doesn’t disclose much —
Turns out both issue can be resolve with the above patch notes.
If you try to attach context and it fails, especially the URLS, it is likely due to trying to use the built-in newer version of posthog as noted above. Edit the pre-build script as noted.
If you try to run a chat and get the vector database auth failure, you need a proper NVIDIA API key.
USER_AGENT environment variable not set, consider setting it to identify your requests.
[nltk_data] Downloading package punkt to /home/workbench/nltk_data...
[nltk_data] Unzipping tokenizers/punkt.zip.
[nltk_data] Downloading package averaged_perceptron_tagger to
[nltk_data] /home/workbench/nltk_data...
[nltk_data] Unzipping taggers/averaged_perceptron_tagger.zip.
[config] No INTERNAL_API set.
[config] Using public embedding model: nvidia/nv-embedqa-e5-v5
http://localhost:8000
Running on local URL: http://0.0.0.0:8080
To create a public link, set `share=True` in `launch()`.
IMPORTANT: You are using gradio version 4.15.0, however version 4.44.1 is available, please upgrade.
--------
---ROUTE QUESTION---
How do I add an integration in the CLI?
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langgraph/pregel/retry.py", line 40, in run_with_retry
return task.proc.invoke(task.input, config)
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langgraph/utils/runnable.py", line 464, in invoke
input = step.invoke(input, config)
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langgraph/utils/runnable.py", line 226, in invoke
ret = context.run(self.func, *args, **kwargs)
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langgraph/graph/graph.py", line 95, in _route
result = self.path.invoke(value, config)
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langgraph/utils/runnable.py", line 218, in invoke
ret = context.run(self.func, *args, **kwargs)
File "/project/code/chatui/utils/graph.py", line 269, in route_question
source = question_router.invoke({"question": question})
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_core/runnables/base.py", line 3246, in invoke
input_ = context.run(step.invoke, input_, config)
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_core/language_models/chat_models.py", line 395, in invoke
self.generate_prompt(
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_core/language_models/chat_models.py", line 1025, in generate_prompt
return self.generate(prompt_messages, stop=stop, callbacks=callbacks, **kwargs)
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_core/language_models/chat_models.py", line 842, in generate
self._generate_with_cache(
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_core/language_models/chat_models.py", line 1091, in _generate_with_cache
result = self._generate(
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_nvidia_ai_endpoints/chat_models.py", line 382, in _generate
response = self._client.get_req(payload=payload, extra_headers=extra_headers)
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_nvidia_ai_endpoints/_common.py", line 473, in get_req
response, session = self._post(
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_nvidia_ai_endpoints/_common.py", line 369, in _post
self._try_raise(response)
File "/home/workbench/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/langchain_nvidia_ai_endpoints/_common.py", line 462, in _try_raise
raise Exception(f"{header}\n{body}") from None
Exception: [403] Forbidden
Authorization failed
Failed to send telemetry event ClientStartEvent: capture() takes 1 positional argument but 3 were given
Failed to send telemetry event ClientCreateCollectionEvent: capture() takes 1 positional argument but 3 were given
[upload] Vectorstore creation failed: [403] Forbidden
Authorization failed